Identifying vftables through MS's C++ RTTI
Run-Time Type Information or RTTI, is a mechanism that exposes object types information at runtime, used to do safe typecast, using dynamic_cast<> and to manipulate type information using typeid operator and std::type_info class at runtime.
There are some RTTI data structures, but in this post we will see two of them, almost some fields are importants to know class C++ inherintance relationship, class name, and polymorphism but they probably will be treated in a future post. To clarity, I’d like to mention that MSVC 64-bit compiler has definied _RTTI_RELATIVE_TYPEINFO by default. In addition, Visual Studio has /GR compiler option enabled by default to add run-time type information.
typedef const struct _s_RTTICompleteObjectLocator {
unsigned long signature;
unsigned long offset;
unsigned long cdOffset;
#if _RTTI_RELATIVE_TYPEINFO
int pTypeDescriptor; // Image relative offset of TypeDescriptor
int pClassDescriptor; // Image relative offset of _RTTIClassHierarchyDescriptor
int pSelf; // Image relative offset of this object
#else
TypeDescriptor* pTypeDescriptor;
_RTTIClassHierarchyDescriptor* pClassDescriptor;
#if VERSP_WIN64 // TRANSITION, VSO#515783
const _s_RTTICompleteObjectLocator* pSelf;
#endif // VERSP_WIN64
#endif
} _RTTICompleteObjectLocator;
typedef struct TypeDescriptor
{
#if defined(_WIN64) || defined(_RTTI) || defined(BUILDING_C1XX_FORCEINCLUDE)
const void * pVFTable; // Field overloaded by RTTI
#else
unsigned long hash; // Hash value computed from type's decorated name
#endif
void * spare; // reserved, possible for RTTI
char name[]; // The decorated name of the type; 0 terminated.
} TypeDescriptor;
RTTICompleteObjectLocator is used as the first entry to uses typeid operator, dinamic_cast<>, calculate member offsets and get multiple, virtual and single-inherintace hierarchy. TypeDescriptor is a structure that allows the use of typeid operator through std::type_info class.
To purpose of this blogpost, I’ll use the following code:
struct A { int a; };
struct B : virtual A { virtual void f() { puts("im f"); }; int b; };
The this object will have as many fields as there are class members. Almost, when RTTT is used the first field is a pointer to its vtable, also known as vfptr, and we can get RTTICompleteObjectLocator pointer at vfptr[-1]: static_cast<_RTTICompleteObjectLocator***>(pointerToObject)[0][-1];. Let’s see the layout of our example.
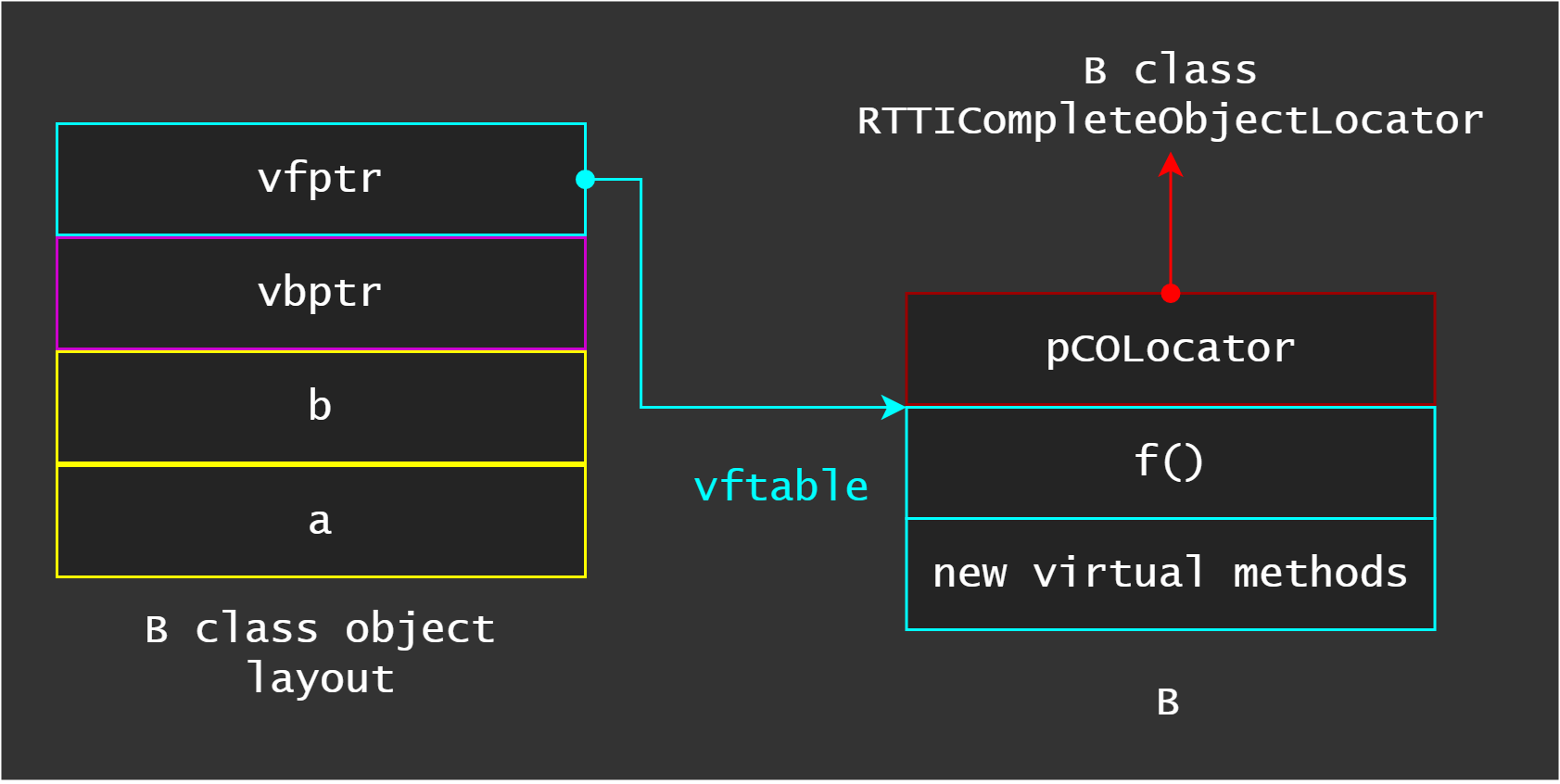
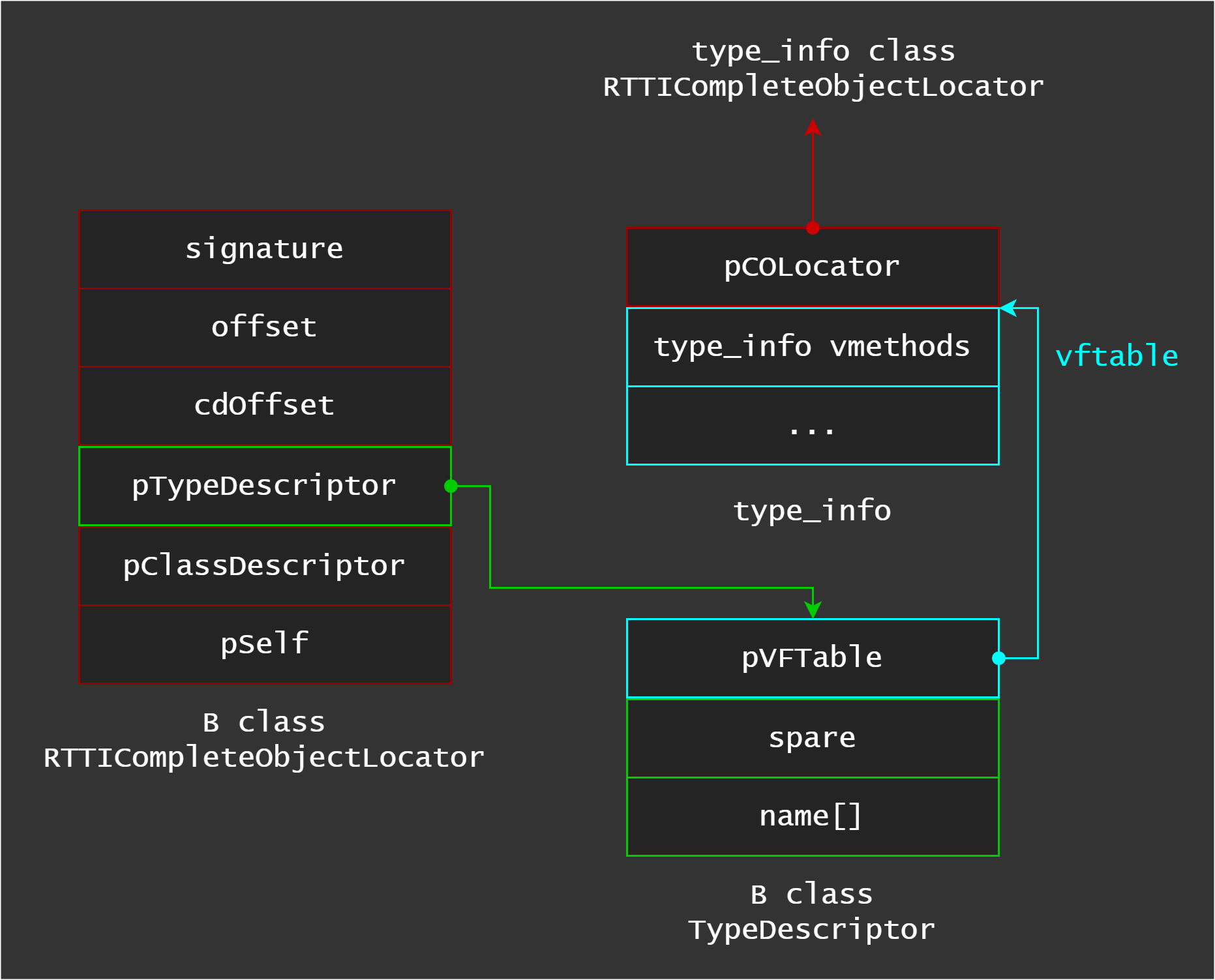
As we can see, pCOLocator points to B::RTTICompleteObjectLocator and from there we can walk to TypeDescriptor structure. The TypeDescriptor structure has a field called pVFTable, and it points to type_info::vftable. So, we can conclude every RTTICompleteObjectLocator structure can be found if we get type_info::vftable address and walk backwards.
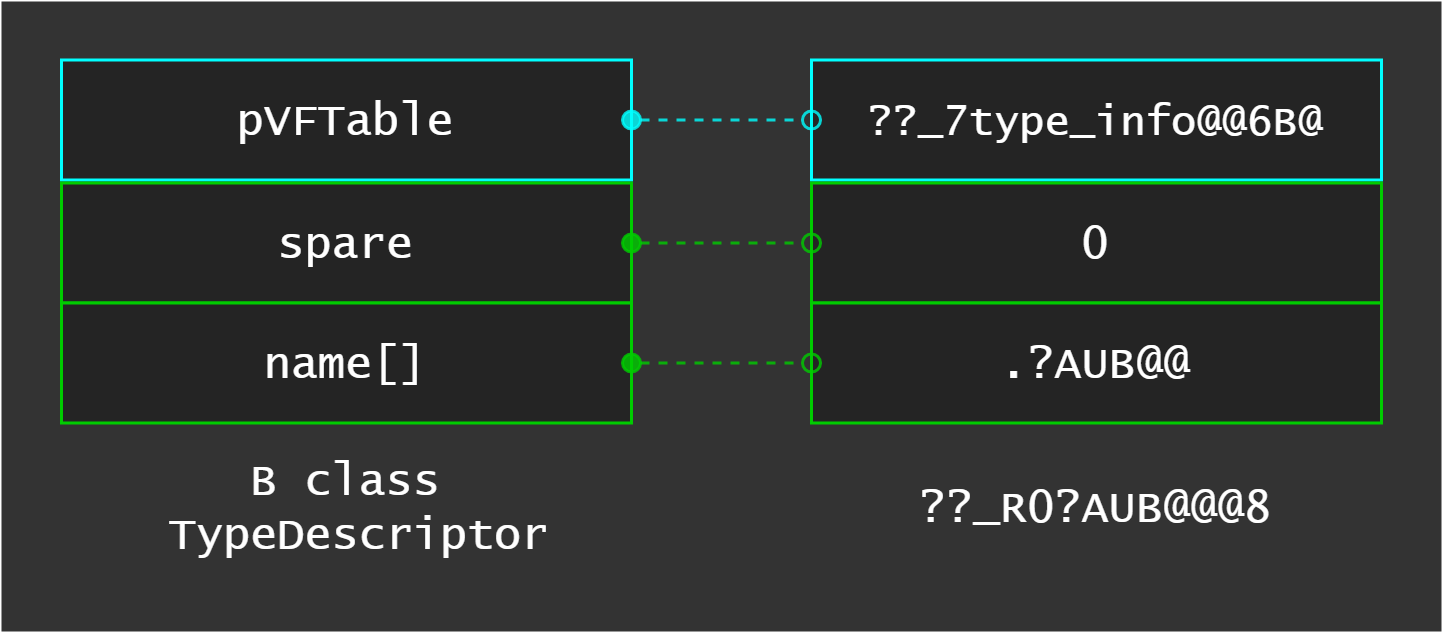
What’s the B::TypeDescriptor values?
Basic MS name mangling
MS-ABI isn’t documented, but we have effors like Clang/LLVM to make compatible compilers. MS-ABI has some symbol prefixs for vftables, RTTICompleteObjectLocator, TypeDescriptor, etc. For example, the mangled name of type_info::TypeDescriptor is ??_R0?AVtype_info@@@8.
# MS-ABI
MS_ABI_VFTABLE_PREFIX = "??_7" # vftable
#MSVC_ABI_VBTABLE_PREFIX = "??_8" # vbtable
MS_ABI_RTTI_COL_PREFIX = "??_R4" # RTTI Complete Object Locator
MS_ABI_RTTI_TD_PREFIX = "??_R0" # RTTI Type Descriptor
MS_ABI_RTTI_BCD_PREFIX = "??_R1" # RTTI Base Class Descriptor
MS_ABI_RTTI_BCA_PREFIX = "??_R2" # RTTI Base Class Array
MS_ABI_RTTI_CHD_PREFIX = "??_R3" # RTTI Class Hierarchy Descriptor
# type_info::TypeDescriptor mangled name
TYPEINFO_TD_MANGLED_NAME = "??_R0?AVtype_info@@@8"
vftables lookup
As I said before, the key to find vftables is type_info::TypeDescriptor structure because type_info::TypeDescriptor.pVFTable points to type_info::vftable (its mangled name is ??_7type_info@@6B@). In the following image you can see structure relationship
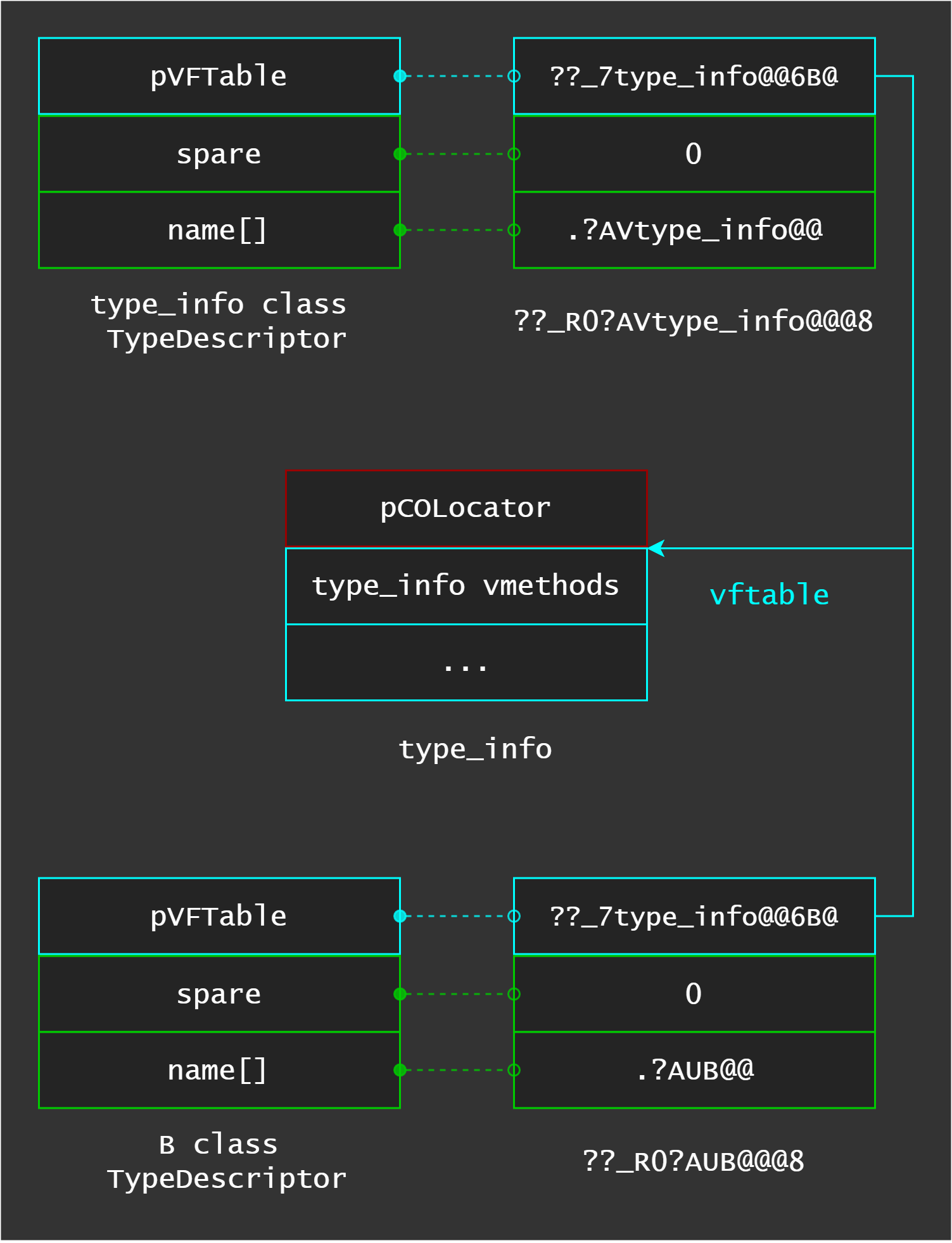
In resume, we need the type_info::vftable address, to get whole crossreferences because every type_info::TypeDescriptor.pVFTable field structure points there. After that, get the crossreferences of type_info::TypeDescriptor because RTTICompleteObjectLocator.pTypeDescriptor points there. Finally, get the whole crossreferences of RTTICompleteObjectLocator to get the address one by one, add it sizeof(void*), compare if the prefix is '??_7 and reach our goal, get whole vftables :D.
- Lookup
type_info::vftableaddresstype_info_vftable_addr = helper.read_xword( ida_name.get_name_ea( idaapi.BADADDR, TYPEINFO_TD_MANGLED_NAME)) - Get
type_info::TypeDescriptorcrossreferencestype_descriptor_xrefs = helper.get_xrefs_to(type_info_vftable_addr) - Search
RTTICompleteObjectLocatorthroughtype_info::TypeDescriptorcrossreferencesfor type_descriptor_xref_addr in type_descriptor_xrefs: # possible RTTICompleteObjectLocator.TypeDescriptor rtti_col__type_descriptor_xrefs = helper.get_xrefs_to(type_descriptor_xref_addr) for rtti_col__type_descriptor_xref_addr in rtti_col__type_descriptor_xrefs: # possible beginning of RTTICompleteObjetLocator rtti_col_addr = rtti_col__type_descriptor_xref_addr \ - RTTICompleteObjectLocator().offsetof('type_descriptor') rtti_col_mangled_name = idaapi.get_name(rtti_col_addr) # detect whole RTTICompleteObjectLocator and save them if rtti_col_mangled_name.startswith(MS_ABI_RTTI_COL_PREFIX): self.rtti_col_list.append((rtti_col_addr, rtti_col_mangled_name)) - Get whole
vftablesadding theRTTICompleteObjectLocatoraddress +sizeof(void*)for rtti_col in self.rtti_col_list: rtti_col_xrefs = helper.get_xrefs_to(rtti_col[0]) for rtti_col_xref_addr in rtti_col_xrefs: # the vftable are next to RTTICOL vftable_addr = rtti_col_xref_addr + const.EA_SIZE vftable_mangled_name = idaapi.get_name(vftable_addr) # detect whole vftables and save them if vftable_mangled_name.startswith(MS_ABI_VFTABLE_PREFIX): self.vftable_list.append((vftable_addr, vftable_mangled_name)) - Output
[IDACode] Executing d:\c++_research\rtti_parser\rtti_parser.py const std::bad_alloc::`vftable' at 0x1400032c8 const std::exception::`vftable' at 0x140003298 const std::bad_array_new_length::`vftable' at 0x1400032f0 const type_info::`vftable' at 0x140003278 const B::`vftable' at 0x140003358Future work
There is a case where doesn’t exist Run-Time Information Type but vftables are used, and I would like to handle that case. Furthermore, get the inherintance relationship hierarchy.
Written by Nox
